Walther ETR3

Walther ETR3
Distinctive features: One of the first hand-held, battery powered calculators.
Technical details:
Display is 8 digits, "Nixie"-type tubes.
Four-function.
6v rechargeable battery.
Integrated circuits: 6-integrated circuit set from Electronic Arrays of the U.S.A. which may have been manufactured under a second-source agreement by Mullard, a Philips subsidiary. Here they have date-codes of late 1970 and early 1971.
151 mm x 210 mm x 56 mm. (5.9" x 8.25" x 2.2").
Introduced about 1971.
Made in Germany.

With the casing removed showing the miniature NEC LD8007 "Nixie"-type display tubes, the large rechargeable battery, and the keyboard (which covers the main circuit board).

The miniature NEC LD8007 "Nixie"-type display tubes.

A detail of the high-quality, and expensive, keyboard which employs reed-relays (in the glass capsules) activated by magnets on the end of the key stems.
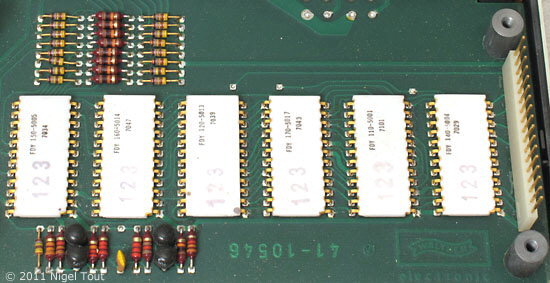
Removing the keyboard reveals the main circuit board with the set of six integrated circuits in ceramic packages designed by Electronic Arrays in U.S.A. They are date coded late 1970 to early 1971.
Hand-holdable, but definitely not a pocket calculator.

Advertisement for Electronic Arrays calculator integrated circuits, from March 1971, which are those used in the Walther ETR3.
Electronic Arrays produced a standard six-chip set for calculators that could be customised by adding other chips, or substituting one or more of the chips, to give extra functions. Using only six chips would offer "reduced labor costs because of the reduced assembly time. This will open up the calculator market to companies that otherwise wouldn't get into it"[1].
The quantity price of the chip set in July 1970 was $60 to $70, but was expected to halve within a couple of years.
The kit consists of an input unit; a control read-only memory; a control logic device, a register, an arithmetic unit; and an output chip, all in 24-pin packages to keep the cost down.
There is further information about the development of the Electronic Arrays chip-set at http://www.oldcalculatormuseum.com/icm816.html.
Hand-held Calculators
Vintage Calculators
Text & photographs copyright, except where stated otherwise, © Nigel Tout 2000-2026.