Sharp QT-8B "micro Compet"

Sharp QT-8B "micro Compet"
Distinctive features: One of the first hand-held, battery powered calculators.
Technical details:
Display is 8 digits, green vacuum fluorescent "Itron" tubes.
Four-function.
The semiconductors of the identical chipset in the Sharp QT-8D was described: "Has four MOS/LSI chips and a clock generator. Each chip contains 900 MOS
transistor equivalents."[1].
"The logic tasks are split up among the four packages. The first, called the NRD 2256, handles the display and
numerical read-in functions. Decimal-point control is taken care of by the second circuit, the DC 2266. The third, AU 2276, handles digital addition and register input control. The fourth the AC 2266, rides herd on the
arithmetic and provides the registers."[2].
7.5v (6x C NiCd rechargeable cells), charging unit provides 12v input.
The calculator alone is 245 x 132 x 70 mm. (9.6" x 5.2" x 2.75").
Was being advertised in the U.S.A in April 1970[3].
Cost in U.S.A. in June 1971 US$495[4].
Made in Japan.
By replacing the AC power supply circuitry of its QT-8D with rechargeable cells Sharp produced this model, the world's first battery-powered electronic calculator.
To recharge the batteries the calculator is docked into a charging unit, shown on the right.
The display uses stylised "Itron" vacuum fluorescent tubes, with half-height zero, here showing 12345670.
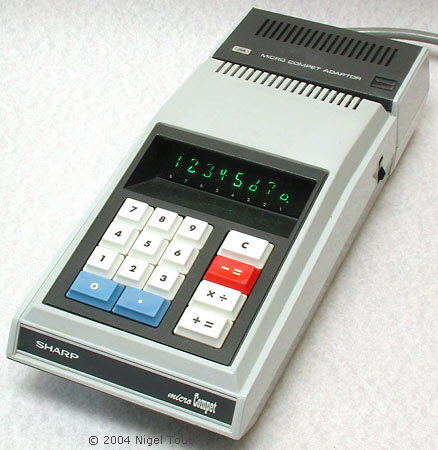
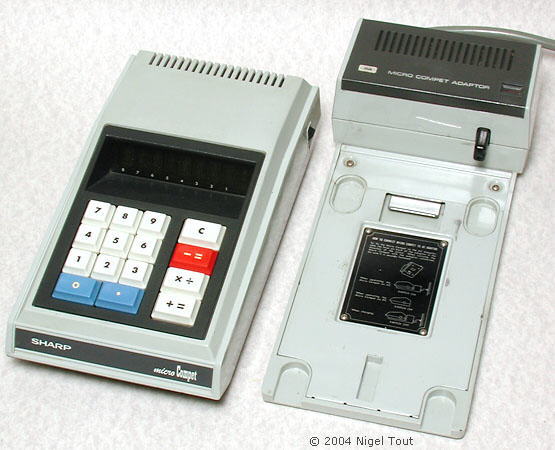


The QT-8B alongside the charging unit.
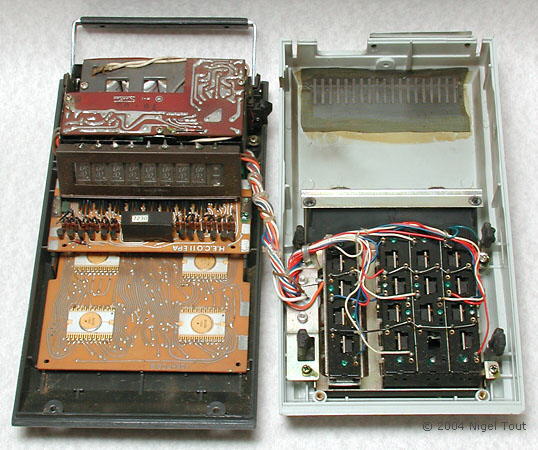

With cover removed, showing the two circuit boards, display, and rechargeable battery compartment.

The four Rockwell integrated circuits on the lower board, with the display board above holding 8 "Itron" numerical display tubes and one "Itron" sign/error display tube.
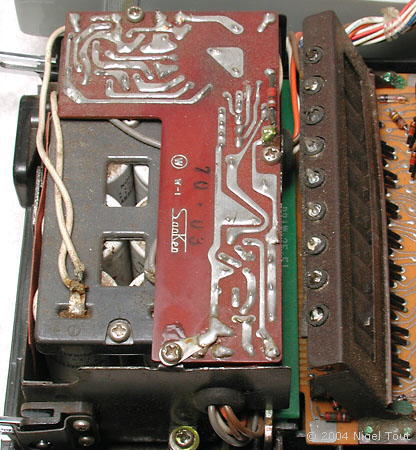
On the left is the battery pack which holds six size C rechargeable cells.
On the right is the display tube assembly.

The rear panel with the plug which accepts 12v DC from the charging unit.


Advertisement for the Sharp QT-8B from June 1970[5].
The Sharp QT-8B has larger rechargeable batteries than the Sharp EL-8 which was launched at about the same time and so is larger.
The development of the MOS LSI chip set is described further in the page about the Sharp QT-8D.
For further information about Sharp Corporation and its calculators visit the Calculator Companies section of this site.
References:
- "Use of LSI in consumer areas picks up, but problems remain", Electronic Design, January 7, 1971, p34.
- Electronics, March 17, 1969, p204.
- Nations Business, March 1970, pp58-59.
- "Microelectronics Shrinks the Calculator", Popular Science, June 1971, p74.
- Electronics, June 22, 1970, p160.
Hand-held Calculators
Vintage Calculators
Text & photographs copyright, except where stated otherwise, © Nigel Tout 2000-2026.